|
|
|
SpecEES: Collaborative Research: Study of the Tradeoff between Spectrum Allocation Efficiency and Operation Privacy in Dynamic Spectrum Access Systems
Two of the key challenges in the design of dynamic spectrum access (DSA) technology are operation security and efficiency in spectrum management. For many federal or government incumbent users (IUs), its operation data are classified. Secondary users (SUs) operation data may also be commercial secret for its operator. Yet, to realize efficient spectrum access, current DSA designs often needs to reveal IUs and SUs's accurate operation data to untrusted third parties, which exposes sensitive IU and SU data to potentially severe privacy violation. A few of existing works have studied privacy and efficiency in DSA separately. However, no exiting work has thoroughly examined these two key challenges jointly. In essence, how to protect IU and SU operation privacy while still ensuring efficient spectrum allocation is still an open problem. In this project, we will provide answers to the above key questions. We will study various existing DSA design options and identify what information that are exchanged in these designs can be potential privacy and security threat to IU/SU and seeking efficient schemes to mitigate these threats. We plan to also thoroughly examine the limitations that different privacy-preserving approaches impose on the design of spectrum allocation scheme so that trade-off between spectrum allocation efficiency and privacy/operation security protection can be identified.
People: Xiaojiang Du (PI), Jie Wu (Co-PI), Yaling Yang (PI).
|
|
Cooperative AI Inference in Vehicular Edge Networks for Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems
This project plans to explore distributed DNN processing scheduling, task assignment, and DNN model parallelism optimization with the consideration of the complex architecture of DNNs and the network environment. Application-wise, the PIs will design novel DNN solutions for ADAS tasks with the coordination of cooperative AI inference paradigm. Testbed-wise, a vehicle edge-computing platform with V2X communication and edge computing capability will be developed at Kettering University GM Mobility Research Center. The cooperative AI inference system will be implemented and the research findings will be validated on realistic vehicular edge computing environments thoroughly.
People: Jie Wu (PI), Ning Wang (PI), Yusheng Wang (PI), Haibin Ling (PI).
|
|
Development of an Information Assurance and Performance Infrastructure for the Internet of Things
This project will develop a novel infrastructure (also referred to as the testbed) to support Information Assurance and Performance (IAP) in the Internet of Things (IoT). The testbed will enable novel research for secure IoT communication, task-resource allocation, robust data storage, and computation offloading in IoT systems.
People: Xiaojiang Du (PI), Jie Wu (Co-PI), Xubin He (Co-PI), Jamie Payton (Co-PI).
|
|
Coexistence of Heterogeneous Wireless Access Technologies in the 5 GHz Bands
Enabling harmonious spectrum sharing between heterogeneous wireless technologies is a challenging problem, but one that needs to be urgently addressed in order to quell the exploding demand for more spectrum by existing as well as burgeoning wireless applications. The main goal of this project is to develop advanced technologies for fair and efficient spectrum sharing between heterogeneous wireless technologies, including LTE-Unlicensed (LTE-U), Wi-Fi (802.11ac/802.11ax), and Dedicated Short-Range Communications (DSRC).
People: Jie Wu (PI), Xiaojiang Du (Co-PI), Marwan Krunz (PI), Jung-Min (Jerry) Park (PI).
|
|
Meso-Scale GENI WiMAX Project
The popularity of wireless networks has led to significant investments in next generation wireless technologies such as WiMAX and LTE. These new technologies promise, among other things, better coverage and higher bandwidth rates, than existing networks. The objective of this project is to build an open, large-scale, outdoor wireless testbed to advance the state of next generation wireless network research. The testbed will be jointly administered by Temple University and Drexel University.
People: Jie Wu (PI), Eugene Kwatny (Co-PI), Shan Lin (Co-PI), Chiu C. Tan (Co-PI)
|
|
Body Sensor Networks and Their Applications in
Maternal Fetal Monitoring
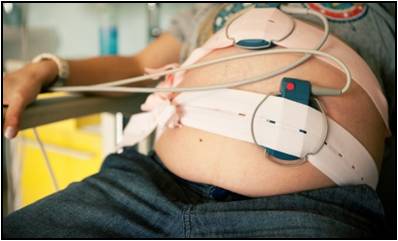
Assessment of fetal health during pregnancy constitutes a very important task of modern obstetrics. It is applied in high risk patients in the third trimester and in almost all patients during labor and delivery. Currently, the monitoring devices needed for fetal heart rate (FHR) and uterine contractions are hardwired to a large monitor (about 15 lbs), and require the patient to remain relatively immobile in order for the monitor to function optimally and continuously. The project seeks to design a body sensor network (BSN), a network consisting of one or more on-body sensing units coupled with a smart local processing unit, to allow normal mobility during the monitored period.
People: Jie Wu (PI), Dimitrios Mastrogiannis (Co-PI)(Medical school), Li Bai (Co-PI)(ECE), Chiu C. Tan (Co-PI)
|
|
Mobile Content Sharing Networks: Theory to Implementation
The last few years have witnessed an explosive growth in the popularity and capabilities of mobile handheld devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. These portable devices rapidly
expanding computational power has enabled their users to access, process, and share content anytime, anywhere. Mobile content sharing has several salient features such as mobility of numerous users, rich content, and individual users ever-growing need for communication and computation capacity. The goal of this project is to investigate how to exploit the key attributes of mobile content sharing environments to dramatically increase network performance.
People: Jie Wu (PI), Xiaojiang Du (Co-PI)
|
|
Hybrid Wireless Network Infrastructure for
Integrated Research and Education
This project seeks to build a Hybrid Wireless Network (HWN) consisting of two WiMAX base stations, forty-eight WiMAX/Wi-Fi mobile stations, one computing server, one storage server, and a Gigabit Ethernet switch. The proposed HWN infrastructure will support research and education in broadband wireless networking and communications, and enable high-quality and high-accuracy performance evaluations of protocols and schemes designed for HWNs.
People:Xiaojiang Du (PI)
|
|
Towards Robust and
Self-Healing Heterogeneous Wireless Sensor Networks
Research has shown that Heterogeneous Sensor Networks (HSN) can significantly improve performance of sensor networks. The objective of this project is to investigate innovative network architectures of HSN, design energy-efficient and self-healing routing protocols, and develop effective security schemes for HSN. Specifically, we will investigate efficient and robust HSN architectures, design self-healing and energy-efficient routing protocols for HSN, and propose effective security schemes.
People: Xiaojiang Du (PI)
|
|
A New Algorithmic and Graph Model for Networking in Challenged Environments
Networking in Challenged Environments (NICE) is designed to meet the special networking needs of the 21st century. These networks operate under special environments which pose unique challenges to the network design. One particular challenge is modeling and analyzing mobility. This project presents a generalized graph model that can capture mobility in NICE. This model is called a weighted evolving graph which captures time-space dynamics while remaining simple enough to maintain most of the elegant structure of the traditional graph model.
People: Jie Wu (PI)
|
|
Energy-Efficient Design in Wireless Networks Using Cooperative Communication
The rapidly increasing capabilities and declining costs of computing and communication devices have made it possible to use wireless networks in a wide range of applications that can improve quality of life, and even save lives. One of the key challenges in the deployment of wireless networks is how to prolong the lifetime of the networks. The project studies energy management techniques for wireless sensor networks. The key idea is that we take advantage of the physical layer design that facilitates the combining of partial information.
People: Jie Wu (PI)
|
|
Dynamic Carrier-Assisted Routing in Mobile Networks
The traditional connection-based approach to mobile networks views node mobility as undesirable. In this project, we consider a mobility-assisted model considers mobility as a desirable feature, where routing is based on the store-carry-forward paradigm with random or controlled movement of mobile nodes. This project will be useful in various applications of mobile networks, including MANETs, WSNs, and DTNs and the proposed study will contribute to making these networks more practical.
People: Jie Wu (PI)
|
|
A Hybrid High-Performance GPU/CPU System
This project is to design and operate a hybrid high-performance GPU (graphics processing unit)/CPU system that will complement existing and future federal and state investments at Temple University and will help drive related research and educational activities. As GPUs are about to become an integral part of mainstream computing systems, the hybrid GPU/CPU system enables support for three groups of applications: traditional CPU-based, GPU-based, and hybrid GPU/CPU-based. The proposed hybrid system enables broader heterogeneous computing by deploying multiple types of computing nodes and allowing each to perform the tasks to which it is best suited.
People: Jie Wu (PI), Saroj K. Biswas (Co-PI), Michael L. Klein (Co-PI), Igor Rivin (Co-PI), Yuan Shi (Co-PI)
|
|
Mobile Multicore Computing
Multicore technology is a breakthrough technology developed in recent years, which extends the lifetime of Moore's Law by changing its applicability from uniprocessors to multicore processors. Multicore technology is entering the mobile phone domain, and the key challenge in mobile multicore phones is making a good tradeoff between performance and power. This project proposes software-oriented approaches including power-aware parallelization of mobile applications and power-aware task scheduling to meet this challenge.
People: Jie Wu (PI)
|
|
An Architecture for Joint Integration of Inter and Intrasession Network Coding in Lossy Multihop Wireless Networks
Maximizing the throughput while achieving fairness among the flows is one of the fundamental research problems in multihop wireless networks. Network coding has emerged as a promising approach to enhance the performance of wireless networks. The goal of this project is to provide a framework to study and deploy intrasession network coding (IANC), where only packets of the same flow or session are coded together, and intersession network coding (IRNC), which exploits the broadcast advantage of wireless links by mixing different flows at intermediate nodes to resolve bottlenecks, jointly under different wireless network settings.
People: Abdallah Khreishah (PI), Jie Wu (Co-PI)
|
|
Auction-based Cloud Computing
Auction-based cloud computing can reliably reveal the true cost of computation. It also promises the ultimate resource efficiency. This project investigates new computational models and methods that can deliver performance and reliability at the same time when acquiring computing and communication components. These sustainable applications should also survive harsh processing environments.
People: Justin Y. Shi, Moussa Taifi, Abdallah Khreishah, Slobodan Vucetic
|
|
Google Docs for Finance Curriculum (uFin Model)
Google Docs provide seamless authentication that traditional spreadsheets do not have. The availability of Google Finance is also a valuable teaching tool. This project investigates the effective use of Google Docs for teaching financial trading courses.
People: : Justin Y. Shi, Michael Bolton (Finance)
|
|
Integrated Data Warehouse with Entity Matching
Integrating heterogeneous data sources concerning the same population requires entity matching using reliable unique identifiers. In practice, this requirement is often broken. This project investigates entity matching methods that can tolerate typos, transposes, aliases and frequently changed mutable properties. We also investigate database clustering technologies for delivering extremely high performance and high availability at the same time when adding components.
People: : Justin Y. Shi, Zoran Obradovic, Joseph Jupin
|
|
Multiresolution Video Streaming with Network Coding
Video streaming over the communication networks requires unique treatments due to its the special properties. First, the video can be divided into multiple layers that represent different resolutions. Second, the recovery of one layer at the destination is meaningless without recovering all of the lower layers by that destination. Network coding has been shown to simplify the operations and enhance the throughput of multicasting. However, network coding has been studied under homogeneous environments where all of the destinations have the same bandwidth from the source. The objective of this project is to study the integration of network coding with a heterogeneous environment where the destinations have different bandwidth requirements. This creates different challenges on how to create the different video layers and how to code them at the intermediate nodes such that every destination can recover the appropriate amount of video layers.
People: Abdallah Khreishah, Jie Wu
|
|
Project 910: Smart Phone and Social Media for Public Safety
Staffing the 911 call portals is a non-trivial financial and technical challenge for law enforcement offices. Although we have many security cameras mounted, we simply do not have enough eyes to watch them 24/7. This project seeks to dramatically enhance per person surveillance ability by leveraging smart phones, web-based security webcams and social media.
People: Justin Y. Shi
|
|
Temple CAVE: Virtual Environments with Motion Analysis
Virtual Reality (VR) technologies are typically used for gaming, simulations and training. We investigate human reactions to 3D visual stimuli. There are many applications. These include physical therapy, medical education, athlete training, scientific visualization and engineering designs. With the advent of low cost 3D TVs and motion sensors, low cost personal CAVEs are also possible. When powered by health social network, these devices may deliver services that are not possible before.
People: Emily Keshner (Public Health), Justin Y. Shi, Haibin Ling
|
|
Temple Elastic HPC Cloud
Not all computing intensive applications can use Linux and batch processing for results. Many require human interactions and different operating systems and different application stacks. The TCloud project investigates sustainable infrastructure for scientific research offering heterogeneous high performance processors and networks and multiple operating systems.
|
Secure Air Force Weather Mobile Application
Source: Air Force Research Lab
Duration: 07-01-2014 to 03-31-2016
Role: Dr. Du is the PI.
|
|
A Test-bed of Secure Mobile Cloud Computing for Military Applications
Source: Army Research Office
Duration: 08-01-2014 to 07-31-2016
Role: Dr. Du is the PI.
|
|
|
Seminars
8/29/2013 Krishna Kant (George Mason University), "Computing at Scale Energy and Robustness Issues", Thursday, August 29, 2 PM, Wachman Hall 1015D
5/3/2013 Liuqing Yang (Colorado State University), "Phasor State Estimation from PMU Measurements with Bad Data", Friday, 2:00pm, Wachman 1050D
3/18/2013 Grace Guiling Wang (New Jersey Institute of Technology), "On-road Localization and Data Dissemination in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks", Monday, 12:30pm, Wachman 1050D
3/4/2013 Chita Das (Pennsylvania State University) DISTINGUISHED SPEAKER, "Performance Tuning in Clouds: A Multidimensional Approach", Monday, 11 AM, Wachman 1050D
2/27/2013 Nan Zhang (George Washington University), "Data Exploration and Privacy Preservation Over Hidden Web Databases", Wednesday, 11 AM, Wachman 447
11/14/2012 Leslie Valiant (Harvard University) DISTINGUISHED LECTURE: "Biological Evolution as a Form of Learning", Wednesday, 11 AM, TECH Center 111
11/29/2012 Don Towsley (University of Massachusetts) DISTINGUISHED LECTURE: "Swarms: First Class Citizens in the Future Internet", Thursday, 11 AM, TECH Center 111
11/2/2012 Wenjin Lou (Virginia Tech), "Scalable and Owner-centric Secure Data Sharing in Cloud Computing", Friday, 11 AM, Wachman 447.
10/24/2012 Xinwen Fu (University of Massachusetts Lowell), "Third Party Wireless Localization: Theory and Implementation", Wednesday, 11 AM, Wachman 447.
10/17/2012 Keqin Li (State University of New York at New Paltz), "Scheduling Precedence Constrained Tasks with Reduced Processor Energy on Multiprocessor Computers", Wednesday, 11AM, Wachman 447.
10/4/2012 Wei Zhao (University of Macau) DISTINGUISHED SPEAKER, "Internet of Things - What and How", Thursday, 10 AM, 1015D
9/26/2012 Boon Thau Loo (University of Pennsylvania), "Declarative Networking", Wednesday, 11 AM, Wachman 447
9/19/2012 Ken Birman (Cornell University) DISTINGUISHED LECTURE: "What Are the Right Roles for Formal Methods in High Assurance Cloud Computing? ", Wednesday, 11AM, TECH Center 111
|